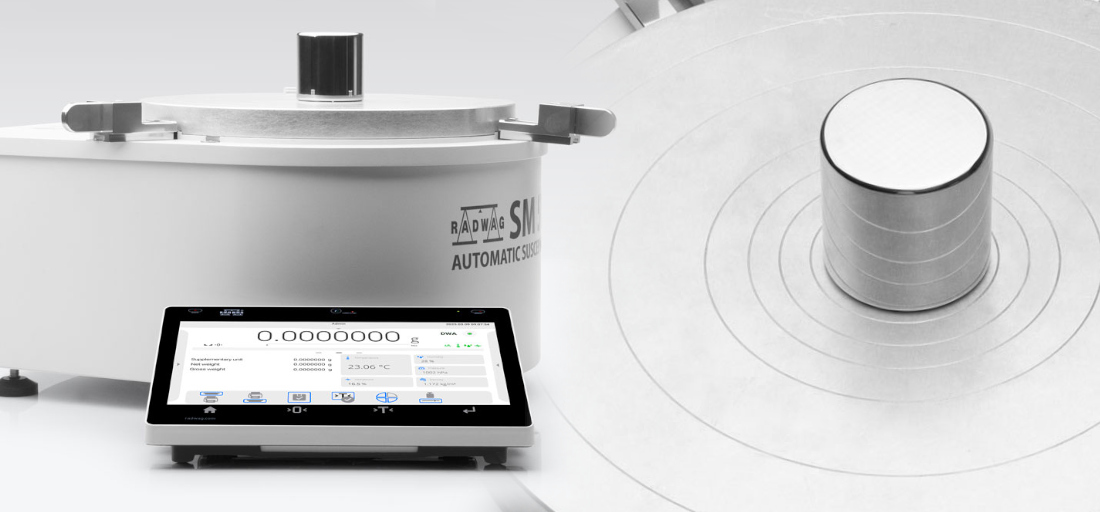
Safety of Mass Measurement in Pharmaceutical Industry. Basic Metrological Tests (part I)

Nowadays many devices are operated intuitively and there is no need to deeply analyse how they work. The balance seems to be an unsophisticated weighing instrument, however, the quite simple weighing process, in terms of manual operation, depends on many factors that may significantly influence the analysis accuracy. The mass measurement, in principle, is not accurate due to imperfect weighing equipment and measurement methods. Satisfying results depend on the mechanical design, ambient conditions and used measurement methods. All these are especially important in pharmaceutical industry where the weighing accuracy is a foundation for medicine quality and savings coming from the research and technological process.
On-Site Installation
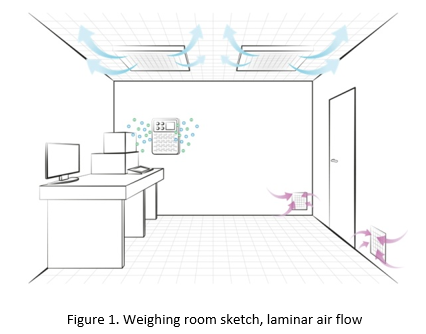
Balance installation is a process in the course of which optimisation of balance operation and ambient condition parameters takes place. The optimisation is done in order to provide satisfying results, namely, such ones that fall within the tolerance limits. The said limits must be set with regard to real requirements for the realised processes. When selecting the site for a balance, a microbalance especially, a few considerations must be taken into account:
- reduced or eliminated air flow,
- rigid construction of the weighing table,
- basis for the balance must be stable, rather ground-supported than wall-fixed,
- the workstation cannot be located in a vicinity of traffic routes and circulation areas,
- installation near windows and sunny areas is disapproved.
Balance Operation and Ambient Conditions
In the case of weighing instrument operation, the ambient conditions are understood as factors relating to the working environment, these are:
- temperature,
- humidity,
- the rate of air flow,
- vibrations,
- unbalanced electrostatic charges in the area of the balance and the sample.
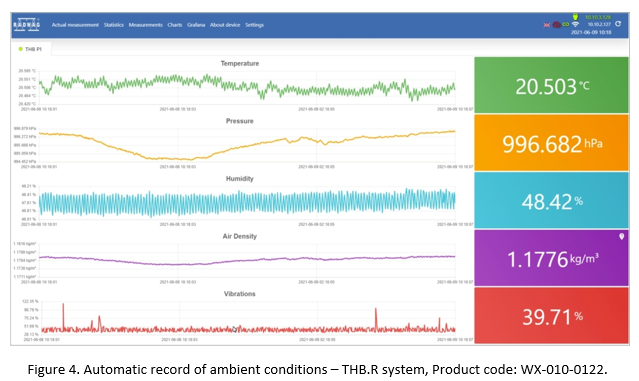
In practice only a few users are enabled to record the dynamics of ambient condition change. Such record is not required when it comes to typical laboratory operations, however, the systems of automatic supervision over the working conditions are becoming more common these days. Radwag product range includes THB sensor, a solution which automatically records temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, air density and ground vibrations. Measurement results can be observed:
- on a balance display,
- online via a website,
- via THB Single or THB Multi application (Windows system),
- via Android system application (mobile).
Unfortunately, it is not easy to assess to what extend the dynamics of ambient condition change influence the weighing result. The simplest evaluation of the balance concerns measurement precision, it is done through determination of standard deviation. Knowing the standard deviation value, one may wonder whether it is possible to obtain even lower result or not. It must be clearly stated that appropriate working conditions for the electronic weighing instrument may be also an effect of use of additional constructional solutions (weighing table, chamber, holder, ionizer) which contribute to weighing room infrastructure.
Adjustment
As it has already been mentioned, there are no perfect measurements. This is due to imperfection of the weighing instruments and used methods. A method is a proven procedure for measuring equipment preparation and measurement performance. It is an approved process (verified with regard to standard-specified and branch regulations), which ensures a precise result providing that all the recommendations are followed, whereby, personnel competences and correct operation of the equipment are taken for granted.
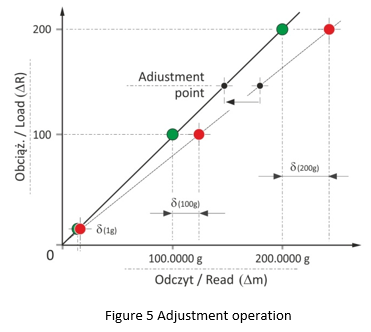
For electronic balances, the mass measurement accuracy depends on correct dependence between the balance load (adjustment mass) and the observed indication. Adjustment aims to correct balance indications, wherein the correction is achieved through comparison of the measurement result, obtained while weighing a so-called adjustment weight, with the certified value of this weight. After completed adjustment, loading of the weighing pan with 200 g weight will result with display of 200.0000 g value. See Figure 5.
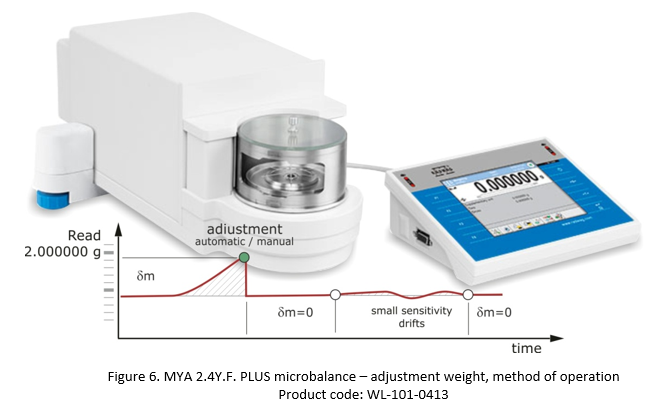
In the case of professional instruments, such as MYA 2.4Y.F PLUS microbalance for example, the adjustment is performed using an internal adjustment weight (Figure 6).
The balance adjustment mechanism monitors temperature changes and time flow online, therefore the adjustment process takes place automatically. Solution of this kind is applied in most electronic weighing instruments manufactured by Radwag. The graph presented in Figure 5 clearly indicates that the potential problem of indication accuracy is significant when the sample mass falls in the range between ½ Max ÷ Max. In the case of small samples of low weight, much more crucial parameter is the indication repeatability. Requirements for repeatability of indications are precisely specified by OIML R-76 (legal metrology) and by the United States Pharmacopoeia, section 41 (Balances), 1251 (Weighing on an Analytical Balance), finally also by the European Pharmacopeia, Section 2.1.7 (Balances for analytical purposes).
Repeatability of balance indication is a persistent feature of a weighing instrument as it is determined by the device construction and the method of measurement signal conversion, however, the repeatability result depends on both, test conditions and operator skills. For this very reason in pharmaceutical industry, it is necessary to monitor not only the technical state of the balance but also the personnel competences. Such approach enables to minimize the risk related to mass measurement; it is advisable to specify the areas of potentially increased risk. The least complicated method of risk assessment is the cause-effect analysis (Figure 7) performed for the weighing process.
Knowing how significant these issues are for the safety of production in the pharmaceutical industry, Radwag offers technical support, in terms of personnel training. Online and face to face cooperation is possible within the scope adequate to the requirements and conducted research.


.jpg)











